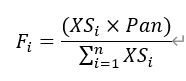光学遥感影像融合

光学遥感影像融合
ytkz一.简介
光学遥感影像融合,需要在几何校正后进行。
二.方法种类
遥感图像融合的方法由最初的一些简单的图像融合法,如加权融合、乘积融合、Brovey变换融合等融合方法,发展到后来出现的一些较为复杂的融合方法,先是塔形算子的提出,后来是小波变换应用到图像融合领域中,再到曲波算法的提出,目前送些算法都还在不同程度的应用于不同的领域。
三.比值变换(Brovey)方法
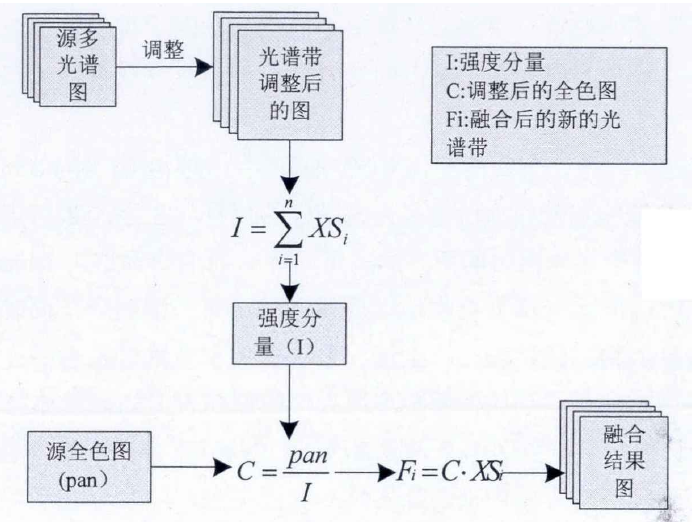
比值运算就是求两张影像或多张影像组合的对应像元灰度值的比值计算,是遥感影像处理过程中经常使用的方法。目前,比值融合算法主要包括Pradines融合法、Price融合法、Brovey融合法以及Munechicka融合法。其中,Brovey融合算法原理是将多光谱各波段影像进行归一化后,再与全色影像进行乘积性的波段运算。由于与色彩空间有关,因此该算法只能对三个波段的影像进行融合处理。
Brovey的流程如下:
Brovey的第一步是调整多光谱影像的大小,使其与全色波段影像的大小保持一致。也就是说:以全色波段的大小为模板,对多光谱影像中的每一个波段的影像进行插值,本文使用gdal提供的方法完成这一步骤,代码如下:
def resample(srcImageFilename,sourceDataset, dstDataset, outname, interp):
# get the "source" (i.e. low-res. multispectral) projection and geotransform
srcProjection = sourceDataset.GetProjection()
srcGeotransform = sourceDataset.GetGeoTransform()
srcNumRasters = sourceDataset.RasterCount
dstProjection = dstDataset.GetProjection()
dstGeotransform = dstDataset.GetGeoTransform()
nrows = dstDataset.RasterYSize
ncols = dstDataset.RasterXSize
dst_fn = outname
# if the resampled-multispectral (3 or 4 band) Geotiff image file exists, delete it.
if not os.path.isfile(outname):
dst_ds = gdal.GetDriverByName('GTiff').Create(dst_fn, ncols, nrows, srcNumRasters, gdalconst.GDT_Float32)
dst_ds.SetGeoTransform(dstGeotransform)
dst_ds.SetProjection(dstProjection)
gdal.ReprojectImage(sourceDataset, dst_ds, srcProjection, dstProjection, interp)
dst_ds = None
del dst_ds
return dst_fn 然后再按照Brovey的公式进行融合。
Brovey的公式如下:
融合代码如下:
def pansharpenBrovey(self,panfile,resampledMultispectralGeotiffFilename,outname):
'''function pansharpenWavelet(self):
This is an instance method that returns a Python list of 3 or 4
NumPy arrays containing the pan-sharpened Red,Green,Blue, and
optionally, NIR bands. These bands will have been created using
the Brovey pan-sharpening method
Returns:
list: Python list[] containing 3 or 4 NumPy arrays using Brovey method.
'''
with warn.catch_warnings():
warn.filterwarnings('ignore', category=RuntimeWarning)
dsPan = gdal.Open(panfile)
dsMulti = gdal.Open(resampledMultispectralGeotiffFilename)
# create output directory to hold .dat files (binary files)
outputDir = os.path.dirname(panfile)
nrows, ncols = dsPan.RasterYSize, dsPan.RasterXSize
red = dsMulti.GetRasterBand(1)
green = dsMulti.GetRasterBand(2)
blue = dsMulti.GetRasterBand(3)
pan = dsPan.GetRasterBand(1)
#设置输出文件参数
# if the multispectal geotiff already exists, delete it.
if os.path.isfile(outname):
os.remove(outname)
Driver = dsMulti.GetDriver()
geoTransform1 = dsMulti.GetGeoTransform()
proj1 = dsMulti.GetProjection()
ListgeoTransform1 = list(geoTransform1)
# write the multispectral geotiff
dst = Driver.Create(outname, ncols, nrows, 3, gdal.GDT_Float32)
dst.SetGeoTransform(geoTransform1)
# dst.SetProjection(dsMulti.GetProjection())
dst.SetProjection(proj1)
for m in range(1, 4):
# self.writeMultispectralGeotiff(sharpenedFIHS, dsMulti, outnameFIHS)
# del sharpenedFIHS
Band = dsMulti.GetRasterBand(m)
outband = dst.GetRasterBand(m)
outband.SetNoDataValue(-9999)
nBlockSize = 1024 * 2 * 2 # 块大小为1024*1024
i = 0
j = 0
# 进度条参数
XBlockcount = math.ceil(ncols / nBlockSize)
YBlockcount = math.ceil(nrows / nBlockSize)
print("第%d波段融合:" % m)
try:
with tqdm(total=XBlockcount * YBlockcount, iterable='iterable', desc='Brovey') as pbar:
while i < nrows:
while j < ncols:
# 保存分块大小
nXBK = nBlockSize
nYBK = nBlockSize
# 最后不够分块的区域,有多少读取多少
if i + nBlockSize > nrows:
nYBK = nrows - i
if j + nBlockSize > ncols:
nXBK = ncols - j
# 分块读取影像
Image_01 = red.ReadAsArray(j, i, nXBK, nYBK).astype(float)
Image_02 = green.ReadAsArray(j, i, nXBK, nYBK).astype(float)
Image_03 = blue.ReadAsArray(j, i, nXBK, nYBK).astype(float)
Image_04 = pan.ReadAsArray(j, i, nXBK, nYBK).astype(float)
Image_00 = Band.ReadAsArray(j, i, nXBK, nYBK).astype(float)
sharp = np.multiply(np.true_divide(
Image_00, Image_01 + Image_02 + Image_03), Image_04)
outband.WriteArray(sharp, j, i)
j = j + nXBK
time.sleep(1)
pbar.update(1)
j = 0
i = i + nYBK
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pbar.close()
raise
pbar.close()
大功告成!
四.可视化
以一景高分一号为例,多光谱影像的空间分辨率为8米,全色影像的空间分辨率为2米。多光谱影像插值前大小为473MB,插值后的多光谱影像大小为7.40GB。
实验1
使用envi打开影像,进行目视对比。
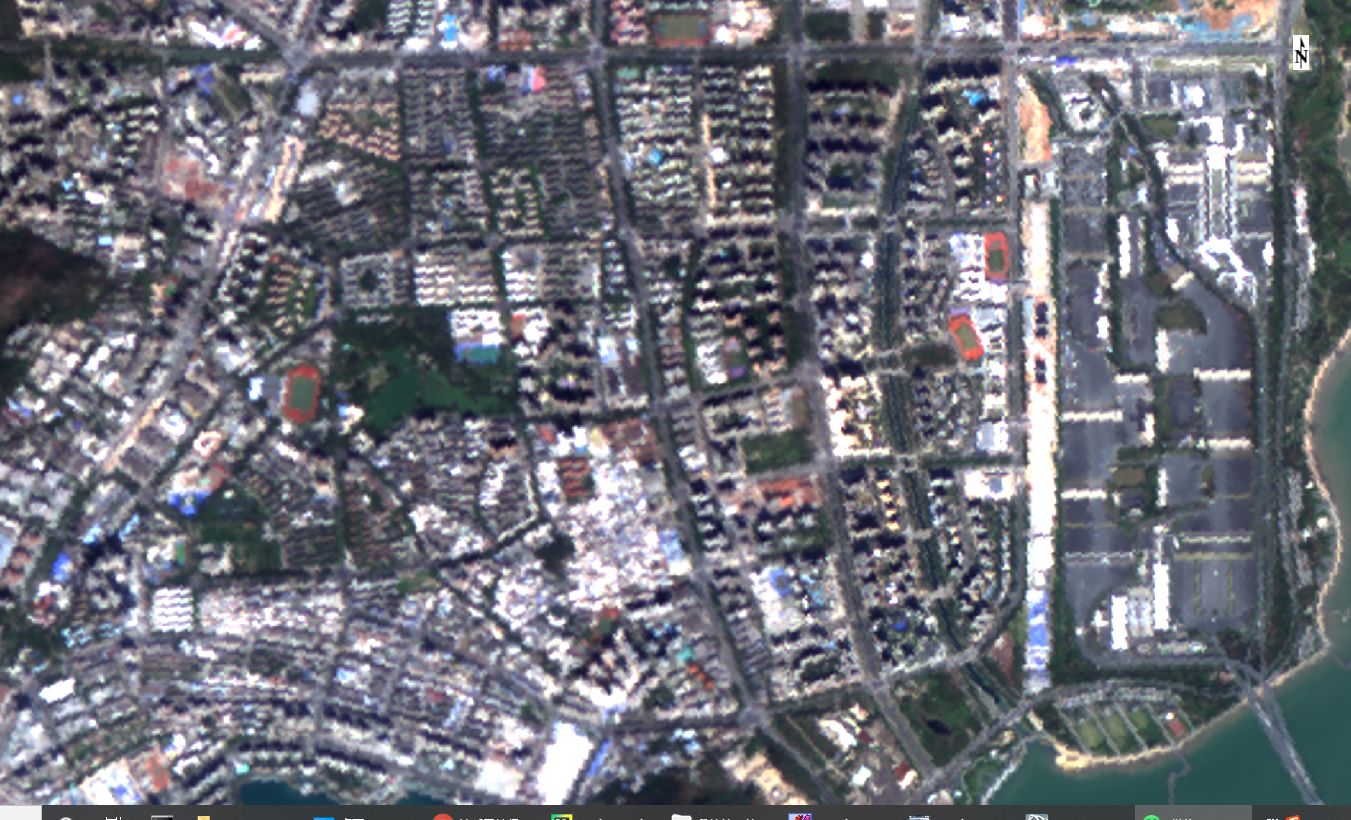
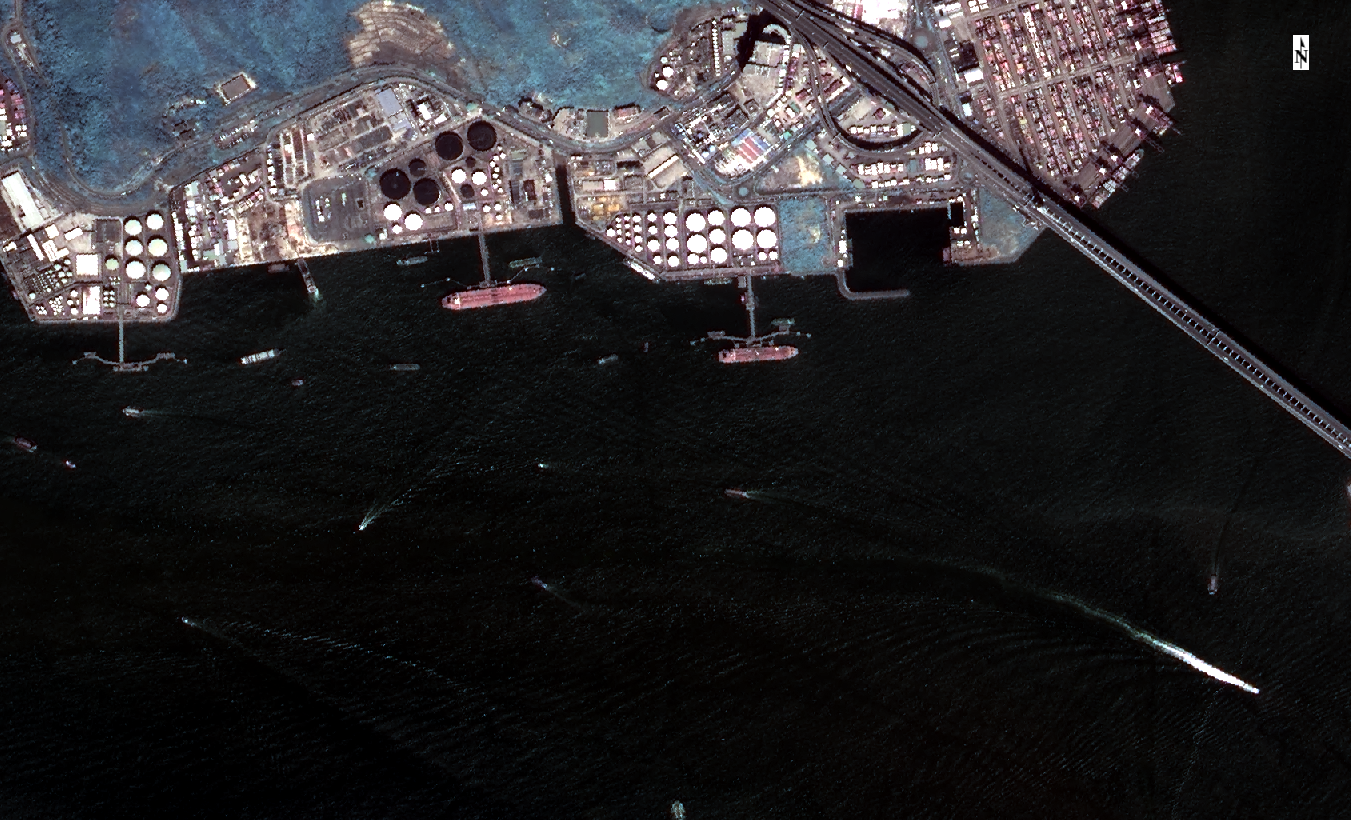
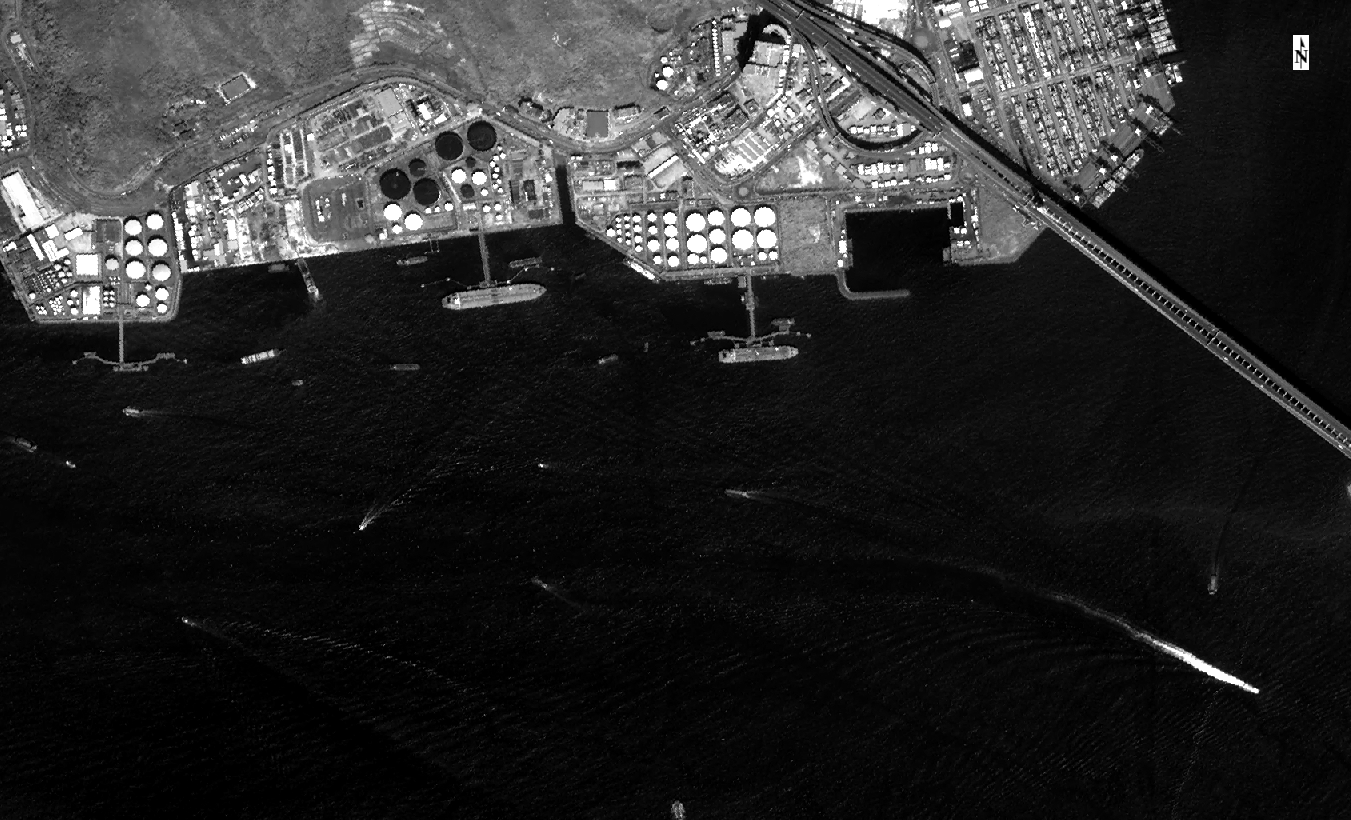
融合前的真彩色图
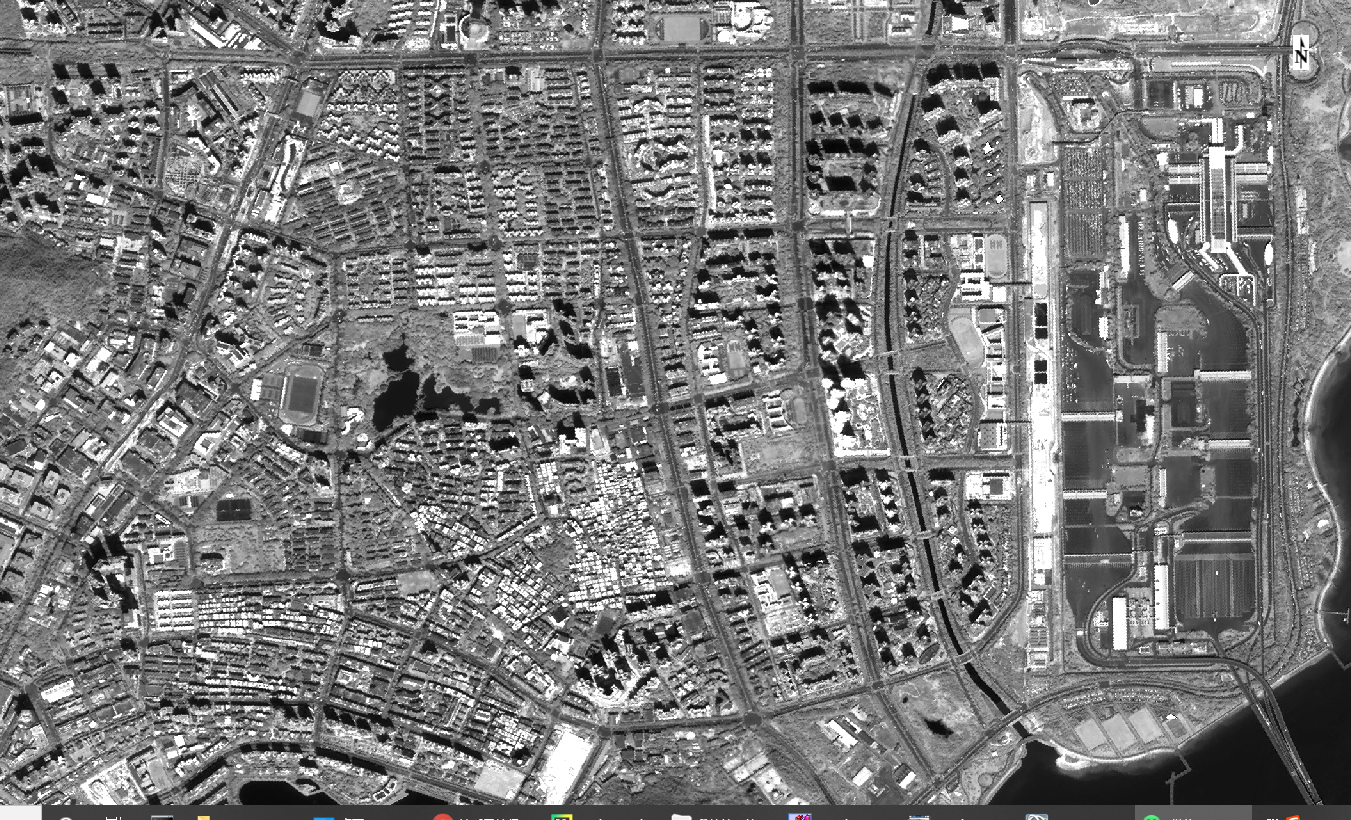
融合前的全色单波段图
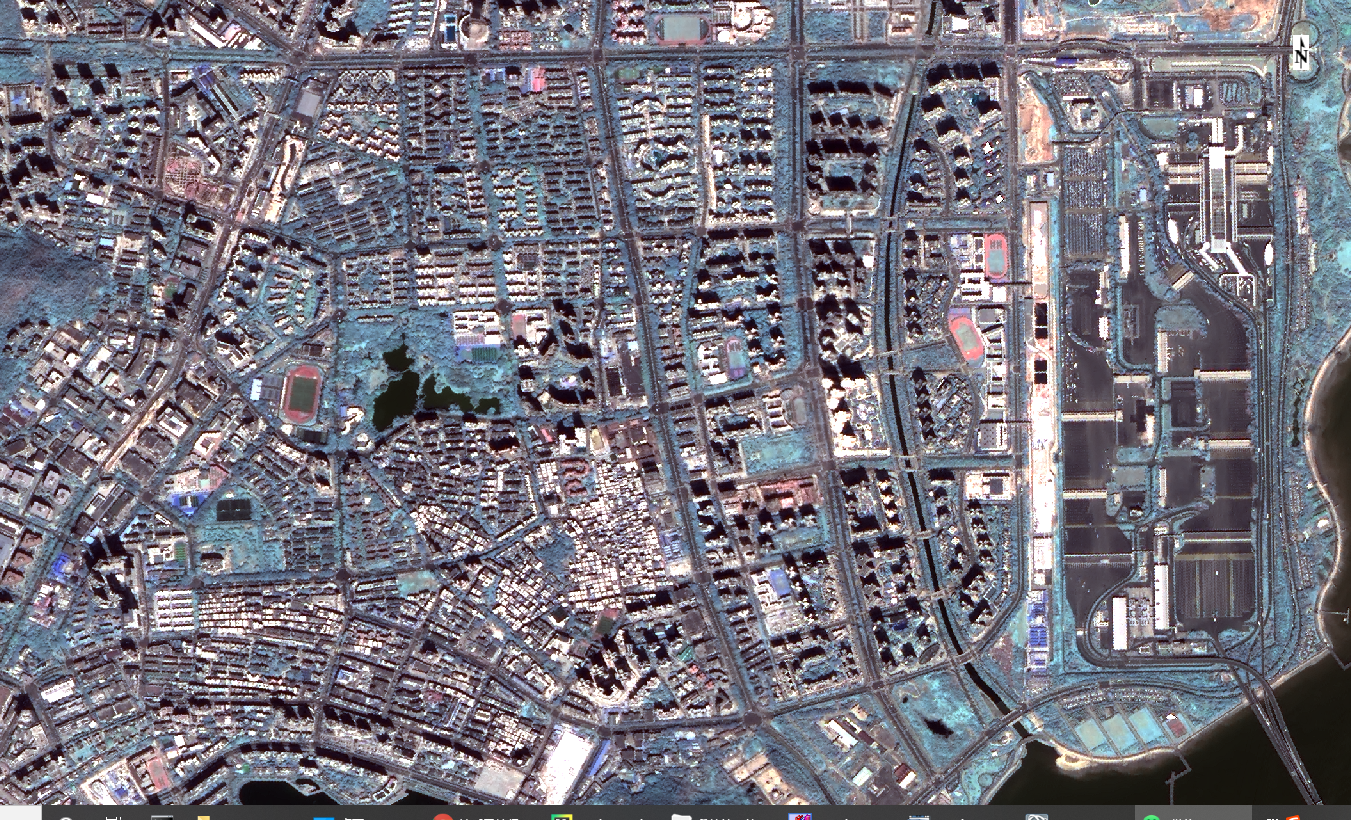
融合后的Brovey融合图
实验2
使用envi打开影像,进行目视对比。
融合前的真彩色图
融合前的全色单波段图
融合后的Brovey融合图
五.小结
使用的数据说明:多光谱影像、全色影像均进行了正射校正(几何校正)。
融合代码中使用了图像分块的思想,这样在低配电脑也能进行遥感影像融合。只是第一步的差值方法是直接调用GDAL的方法,并没有进行分块处理,所以该程序对电脑的性能要求大,特别是内存。
Brovey融合的效果不错,缺点是融合后的影像存在部分视觉色彩偏差。
参考:
[1]王文欣. 多源遥感图像融合技术研究[D].西安电子科技大学,2012.