破损shp文件修复
破损shp文件修复
ytkz大家中秋节快乐!
介绍
半年前写过破损shp文件修复的内容,当时写了一个简陋的小工具。
现在重新讲讲这方面的内容,这篇文章也主要围绕以下两个方面进行展开:
1、当时是怎么实现破损shp文件修复
2、现在怎么把这个功能集成到rstool软件
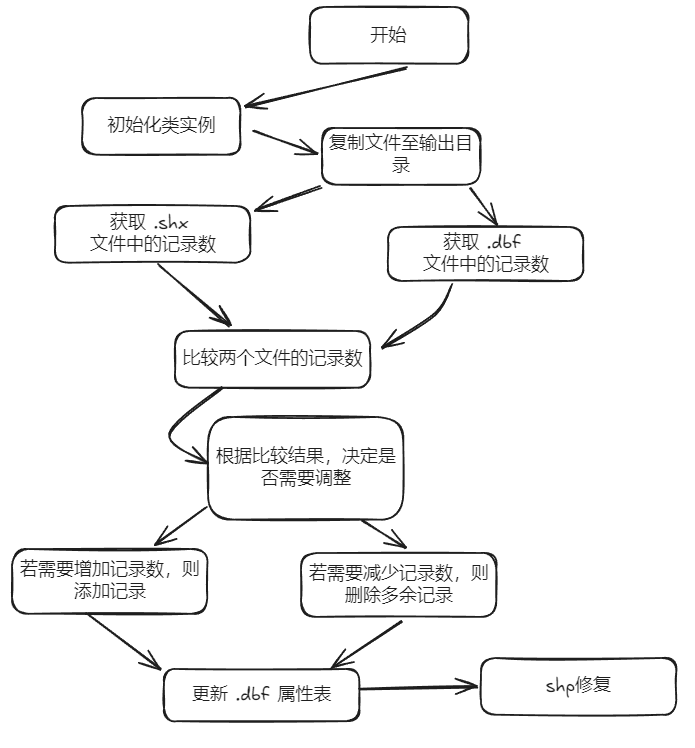
shp文件修复流程
说到shp文件夹修复,必然要讲讲这个问题是怎么出现的。
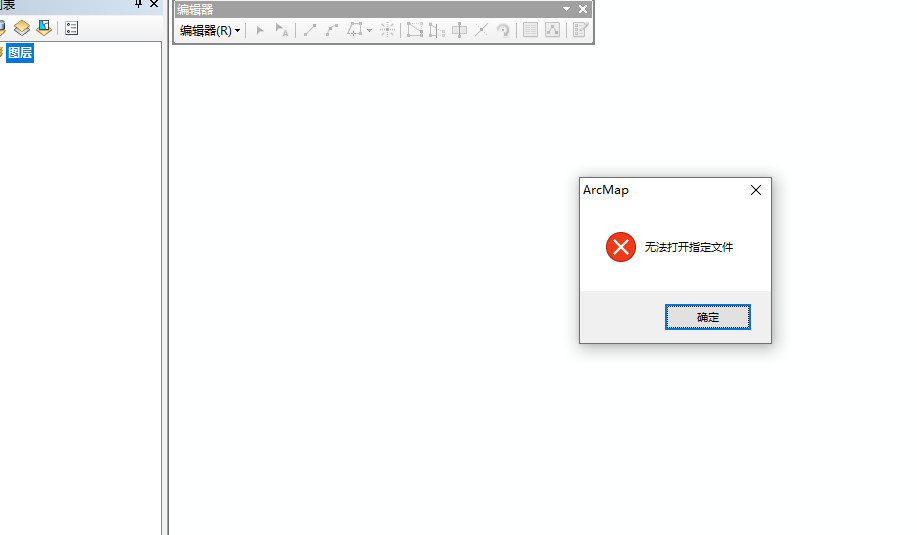
记得某一天,我在愉快的使用着arcgis,正在编辑图斑,由于不可抗力软件闪退了,导致shp文件的图形数量和dbf的属性表数量对不上。
shp的图形是保存在内存里,你画完了一个图形,电脑把这个点位数据自动地保存在.shp文件中,但是属性表需要手动地去完成保存。
如果在你未及时保存文件前,电脑重启了或者arcgis软件大退,就会把整个shp文件打碎,最后把这个矢量文件拖拽到arcgis,显示无法打开。
好了,理解清楚了这个问题的原因,解决思路就很清晰了。
1.修改.shp,使它的图形数量和dbf的属性表个数保持一致。
2.修改.dbf,使它的属性表个数和.shp的图形数量保持一致。
当时选择的方式是第二条,以下是shp修复的流程图
以下代码,是上面的流程的实现(当时为了外国人也看得懂把注释改为了英文。。。)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2024/1/3 20:32
# @File : RestoreShp.py
# 修复shp文件, shp文件中的几何数据和属性数据不一致
import os
import shutil
from struct import unpack
import dbf
class RestoreShp(object):
def __init__(self, file, outpath=None):
self.file = file
self.outpath = outpath
if self.outpath is None:
self.outpath = os.path.dirname(self.file)
if not os.path.exists(self.outpath):
os.makedirs(self.outpath)
if os.path.exists(self.file) is None:
raise Exception('File does not exist')
else:
self.dbffile = os.path.splitext(self.file)[0] + '.dbf'
self.outfile = [os.path.join(self.outpath, os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(self.file))[0] + '_restore.shp'),
os.path.join(self.outpath, os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(self.file))[0] + '_restore.dbf'),
os.path.join(self.outpath, os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(self.file))[0] + '_restore.shx'),
os.path.join(self.outpath, os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(self.file))[0] + '_restore.prj')]
self.copyfile
@property
def copyfile(self):
# 读取shp文件
shutil.copyfile(self.file, self.outfile[0])
shutil.copyfile(self.dbffile, self.outfile[1])
shutil.copyfile(os.path.splitext(self.file)[0] + '.shx', self.outfile[2])
try:
shutil.copyfile(os.path.splitext(self.file)[0] + '.prj', self.outfile[3])
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print('Copy the initial file to the output directory')
def get_shp_shape_records(self):
try:
# First read the geometry data and attribute data of the original file, and return the number of geometric data
self.shx = open("%s" % (self.outfile[2]), "rb")
self.shx.seek(24)
shxRecordLength = (unpack(">i", self.shx.read(4))[0] * 2) - 100
self.numShapes = shxRecordLength // 8
return self.numShapes
except Exception as e:
print(e)
def get_dbf_shape_records(self):
# db = dbf.Dbf(self.dbffile)
with dbf.Table(self.outfile[1], codepage='utf8', default_data_types='enhanced') as table:
pass
return table
def restore_shp(self):
# Number of records read from shp file
shp_numrecords = self.get_shp_shape_records()
# Number of records read from dbf file
table = self.get_dbf_shape_records()
dbf_numrecords = len(table)
# Check whether the number of shp and dbf records is equal
if shp_numrecords != dbf_numrecords:
num = shp_numrecords - dbf_numrecords
if num > 0:
print('The shp file has {} more records than the dbf file'.format(num))
for i in range(num):
table.open(mode=dbf.READ_WRITE)
table.append()
table.pack()
else:
print('The dbf file has {} more records than the shp file'.format(abs(num)))
table.open(mode=dbf.READ_WRITE)
for record in table[shp_numrecords:]:
dbf.delete(record)
table.pack()
if __name__ == '__main__':
file = input('Please enter the path of the shp file: ')
outpath = input('Please enter the path of the output file: ')
if os.path.exists(file) :
record_num = RestoreShp(file, outpath).restore_shp()
print('complete')
else:
print('File does not exist')
input()
破损的shp文件的产生过程
现在手头上没有一个破损的shp文件,但是,但是我们可以构造一个破损的shp文件
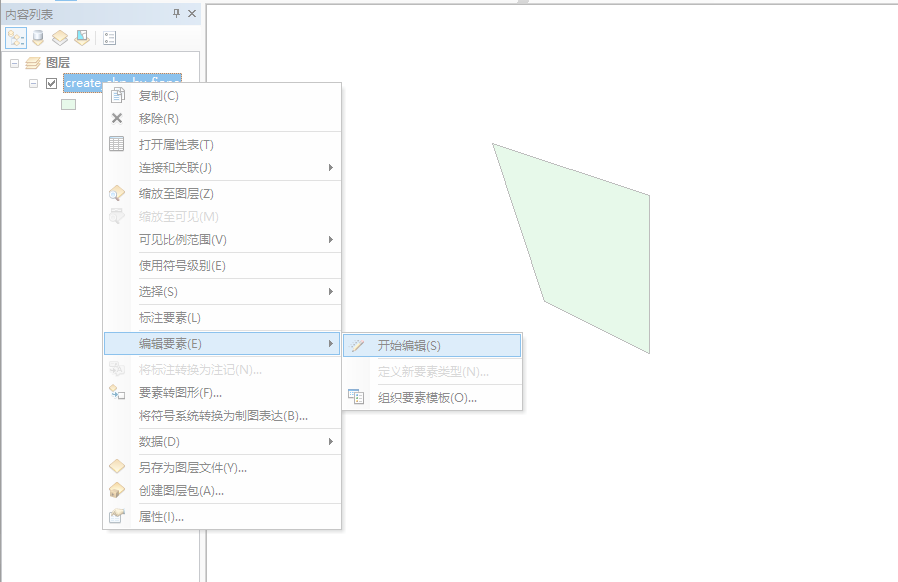
1,复制一个dbf作为临时文件。这个文件待会用到。
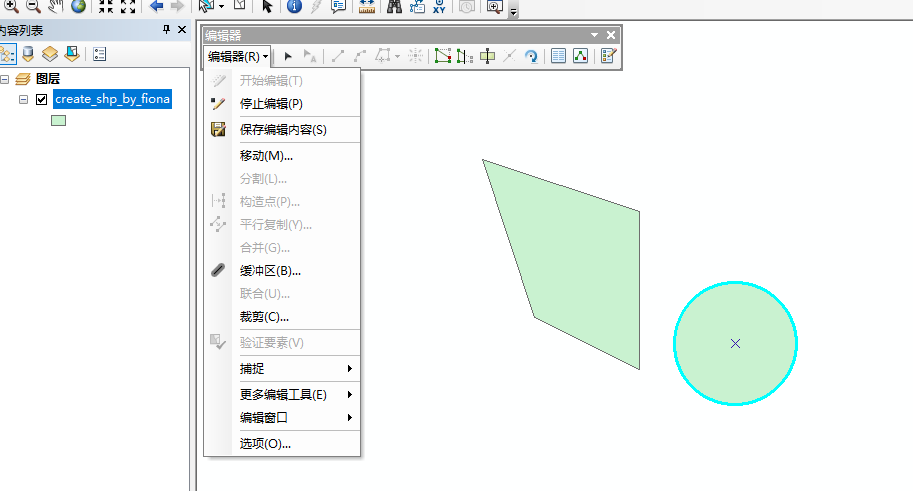
2,在arcgis打开刚刚那个shp,右键它,选择编辑要素,选择开始编辑,如下图
3,画了个圆,点击保存,然后退出arcgis
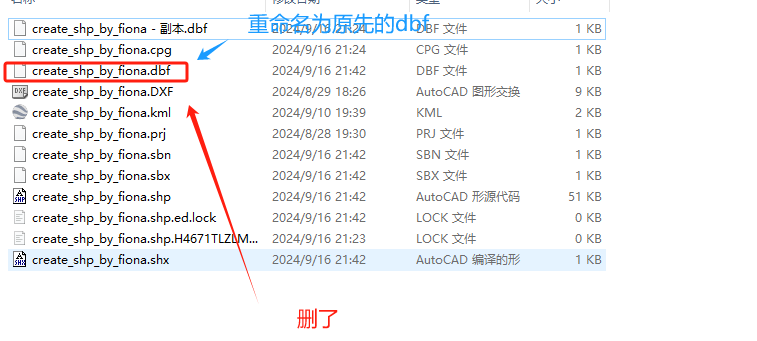
4,把原先的dbf删除,再把一开始的复制的dbf改名为被删除的dbf名字,完成替换。
5,自此,shp文件就变成了破损的shp文件,拖拽到arcgis,就打不开了。
集成rstool的步骤
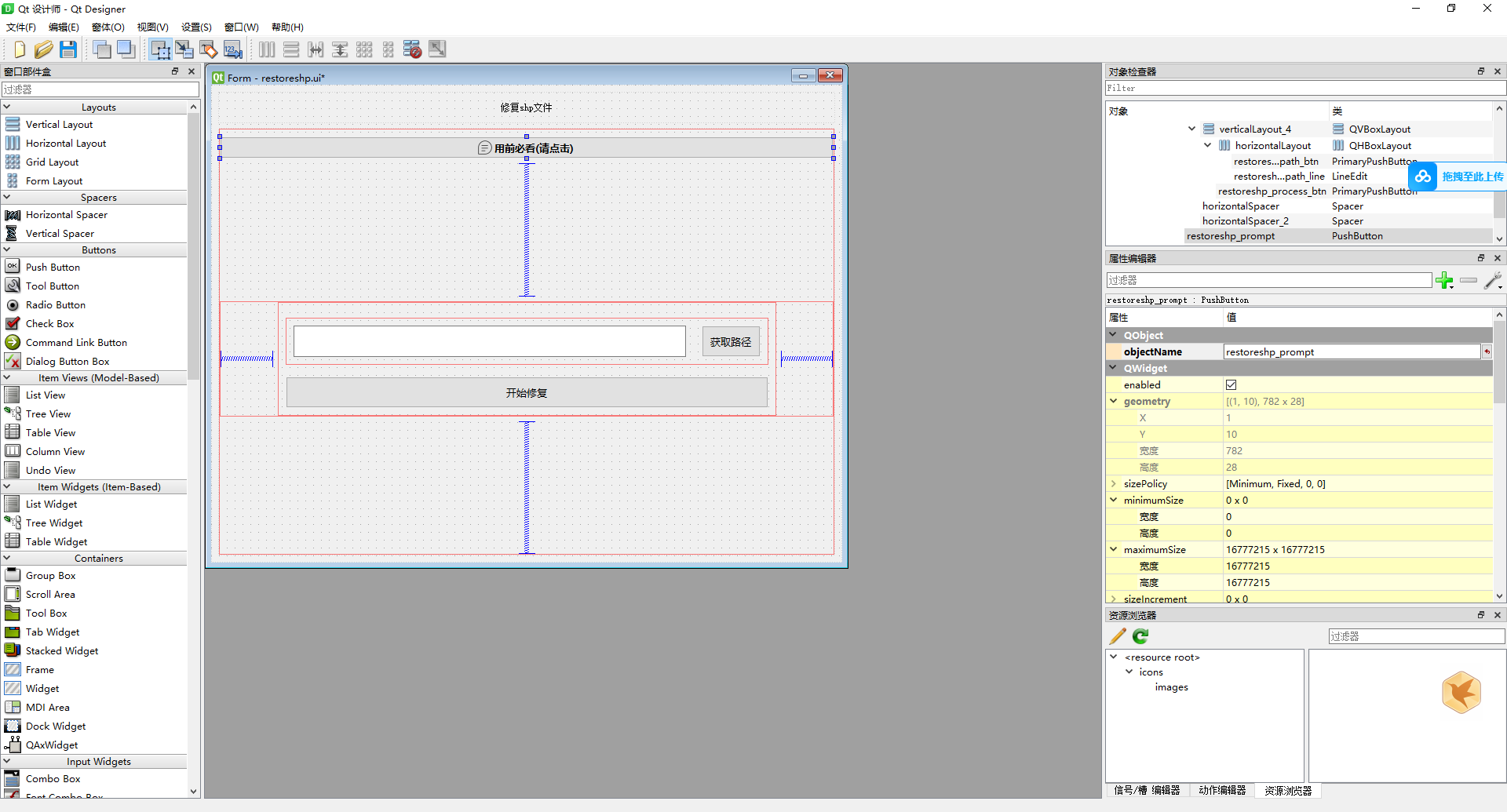
1、在Qt Designer上画好插曲的ui
2、将这个ui文件保存为restoreshp.ui
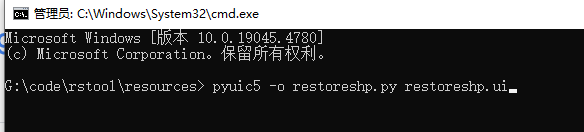
3、在命令行输入:
pyuic5 -o restoreshp.py restoreshp.ui结果如下:
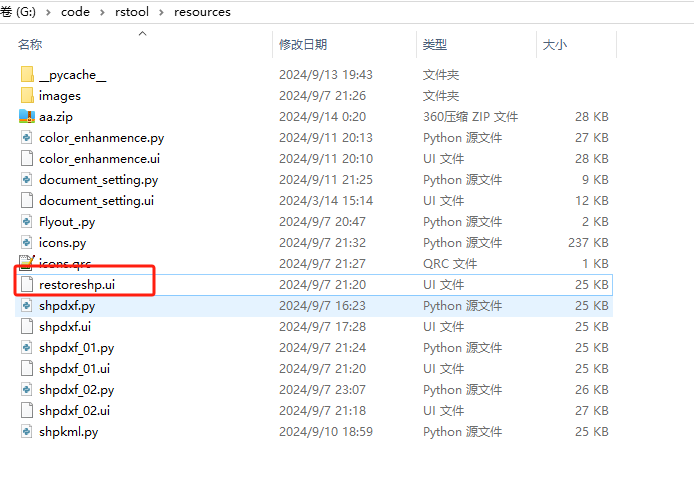
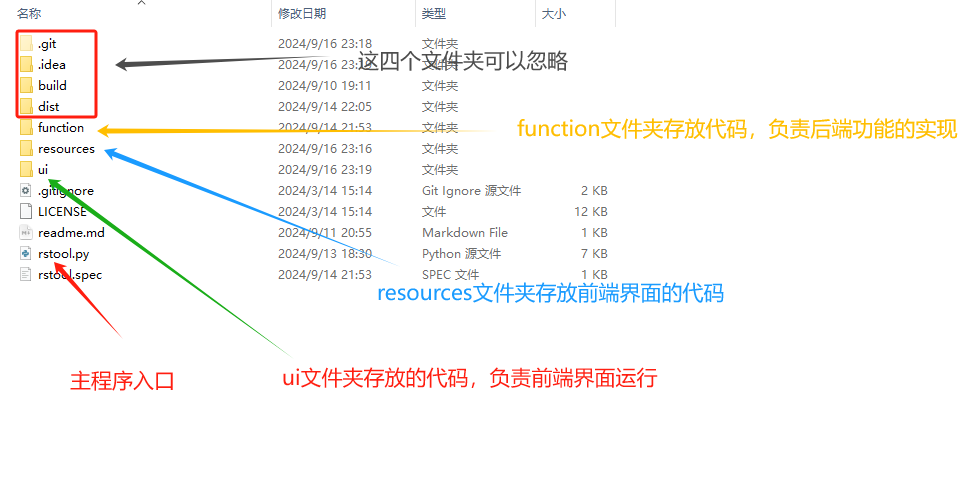
4、在rstool项目中,修改相关代码。我们查看一下rstool整体的结构,如下:
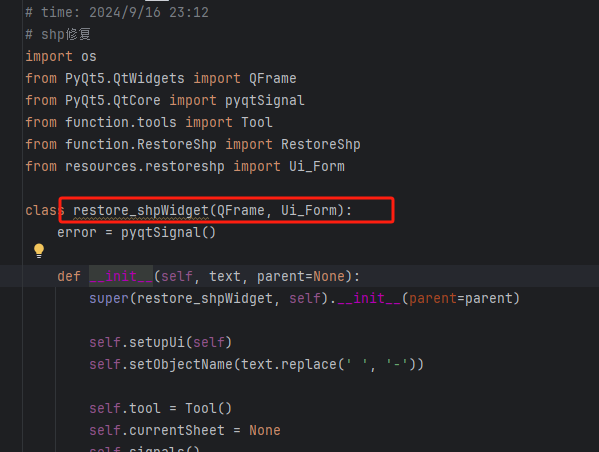
5、在ui文件夹,创建一个叫做ui_restoreshp.py的文件(我直接复制其他已有的文件,这样在已有的基础上进行修改,更节省时间)
先建立一个restore_shpWidget的类,待会用到。剩下的都是体力活了,修改正确的Ui_Form文件的名字,这里不再细说。
6、修改function文件夹下的messages.py文件,这个文件负责前端界面的提示功能
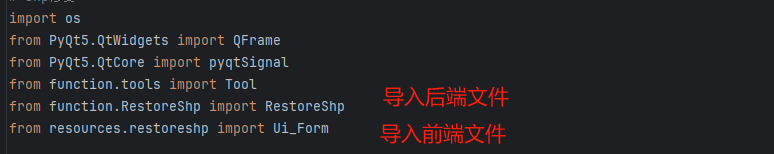
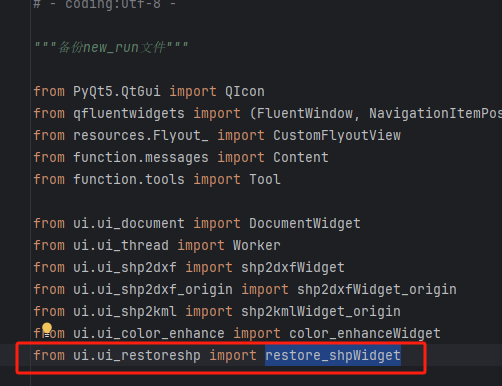
7、修改主程序入口的文件rstool.py,在开头添加一行代码,导入第5步的创建的restore_shpWidget类
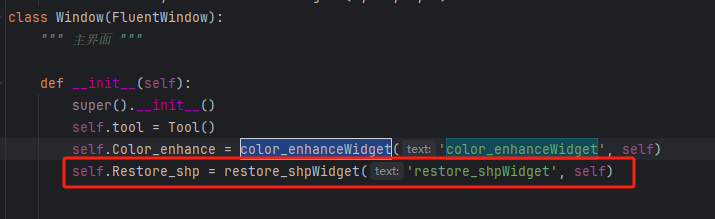
8、在rstool.py中的window类中,增加一行代码,将restoreshpWidget类实例化
9、在rstool.py中的window类中的window_signals函数增加这句,把shp修复界面的按钮以另一个线程的方式串联起来。就是当你点击运行按钮,就在另一个线程运行后端shp修复的函数,这样做的好处是,前端界面不卡顿。
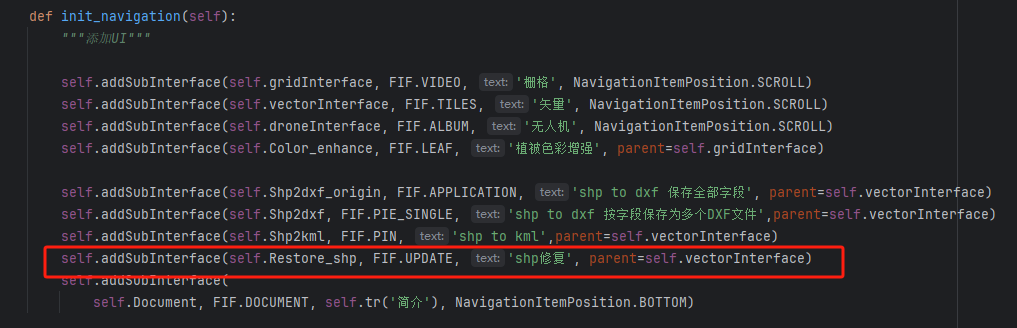
10、在rstool.py中的window类中的init_navigation函数增加这句,目的是在前端的导航栏添加shp修复的菜单。
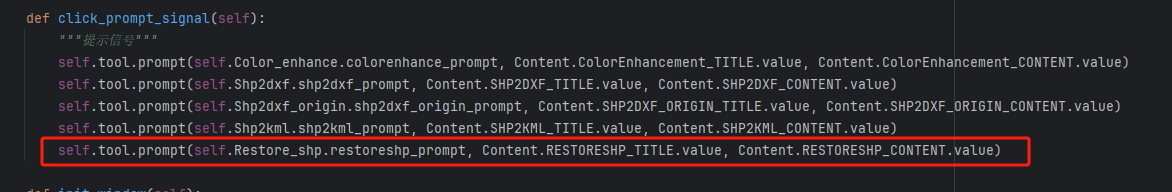
11、在rstool.py中的window类中的click_prompt_signal函数,添加一行代码,把第6步所创建的新增的shp修复的提示功能加载到rstool中。
12、运行rstool.py进行测试,如果遇到报错,则一个错误一个错误去解决。如果没报错,应是如下界面:
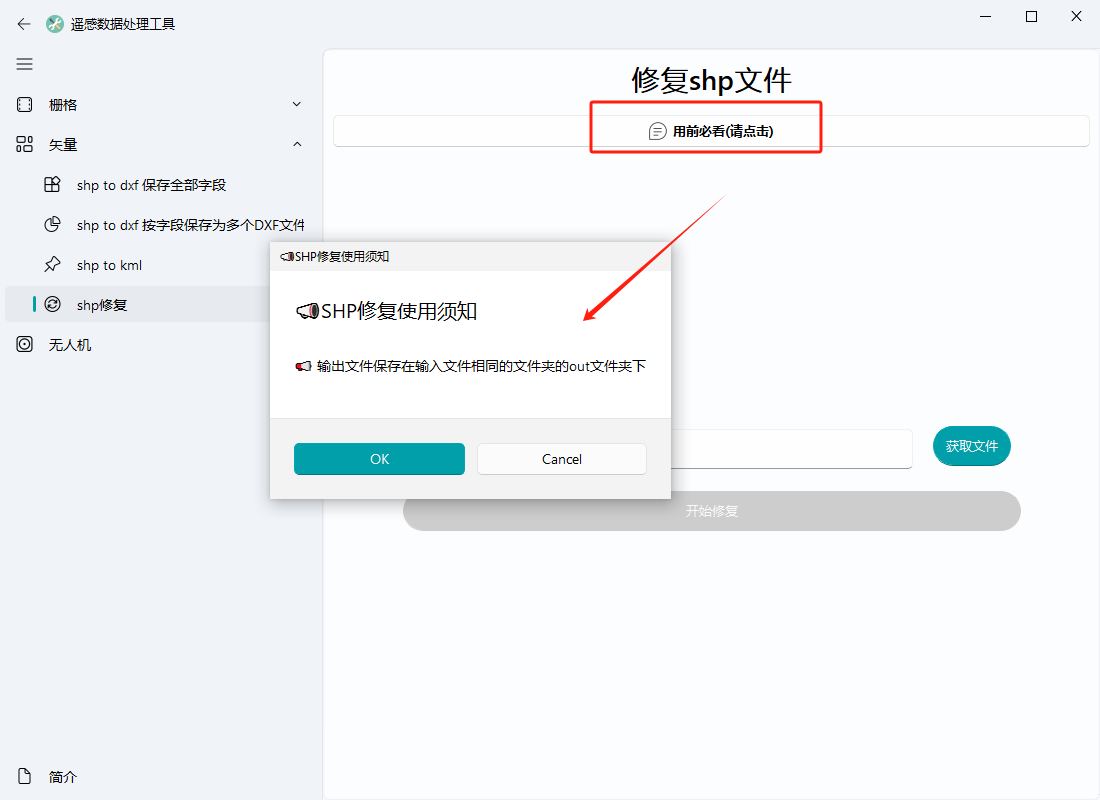
点击“用前必看”按钮,应是如下界面:
接下来进行功能测试。rstool有两种输入参数的方法:
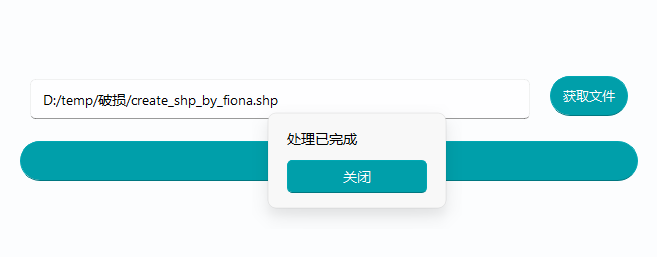
一、点击获取文件按钮,会弹出对话框,让用户选择对应的破损shp文件。
二、直接复制粘贴shp文件的路径到“ 获取文件”按钮的左侧的空白输入框
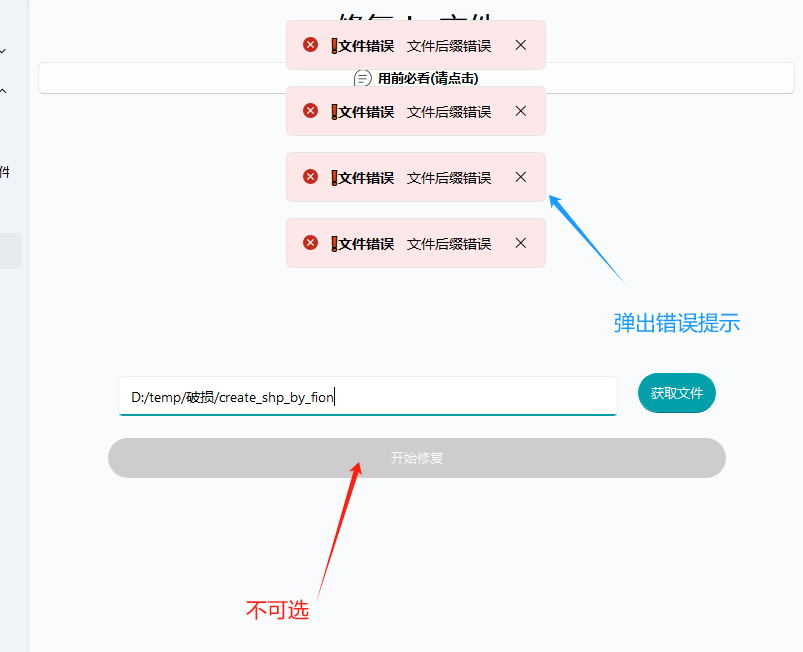
如果你输出的参数有问题,rstool不允许你点击 “开始修复”按钮
shp修复的速度极快,若完成了数据修复,会弹出一个窗口提示 完成数据修复。
修复后的shp保存在D:\temp\破损\out文件夹中,如下所示。此文件夹不需要提前建立。
我们把修复后的shp拖拽到arcgis,测试是否完成修复。
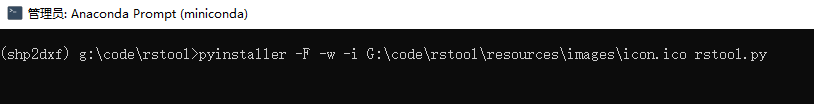
13、在miniconda环境下,使用pyinstaller进行打包,再进行测试。
打包命令是:
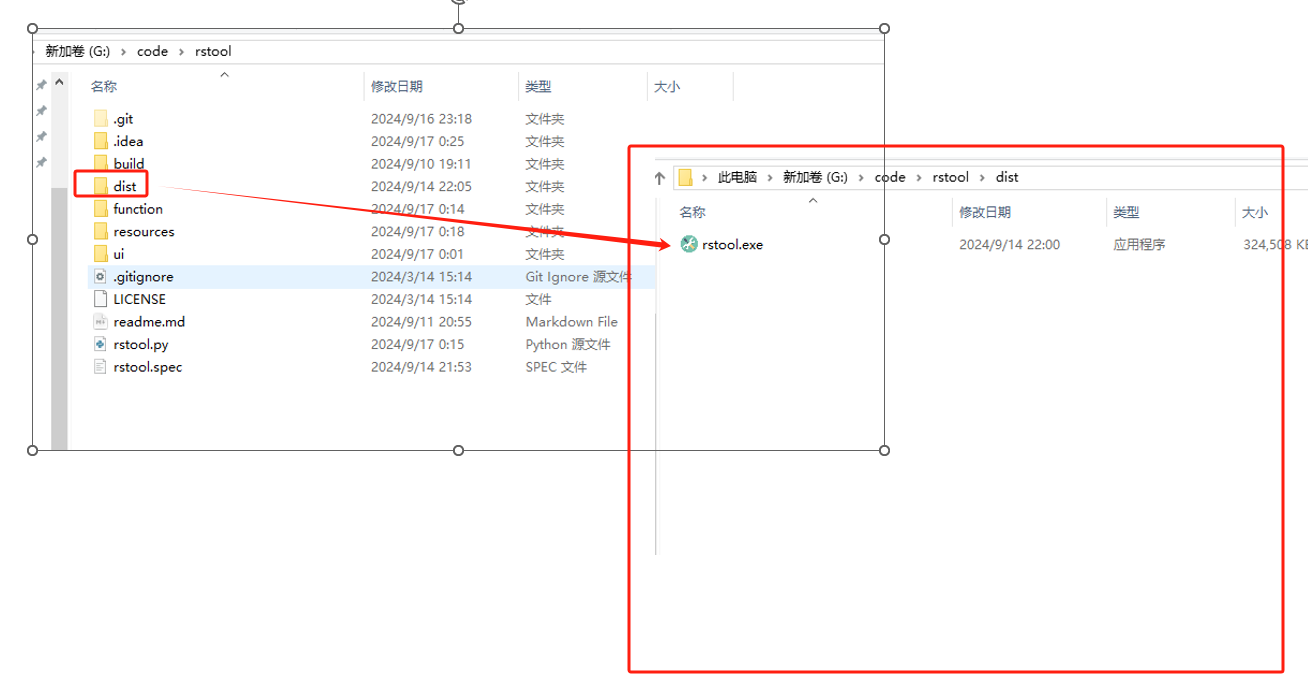
pyinstaller -F -w -i G:\code\rstool\resources\images\icon.ico rstool.py打包完成后,会在dist文件夹生成ratool.exe文件。
我们再次重复第12步的测试。
最后暂时无报错。
测试过程如下:
小结
在后台回复1111获取这个rstool的下载链接。
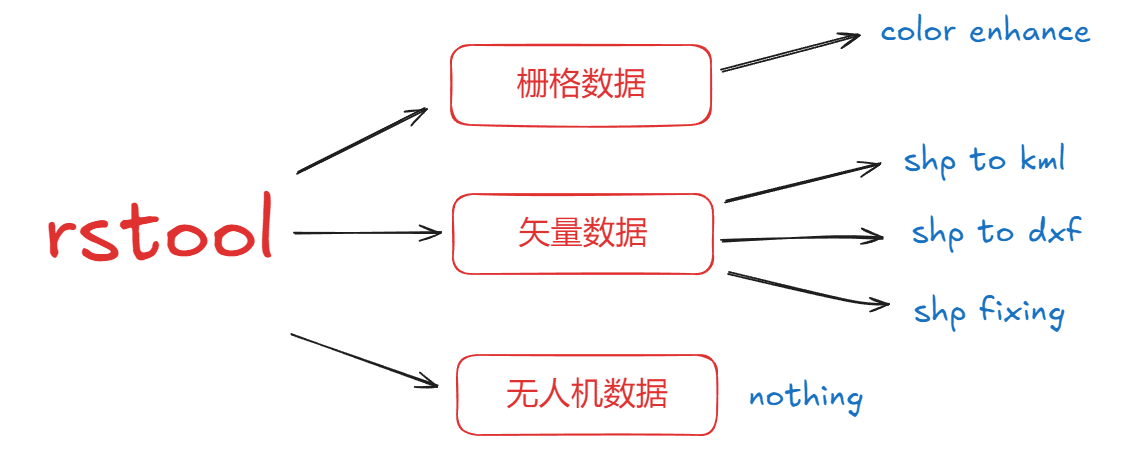
rstool暂时集成了四个功能分别是植被色彩增强、shp转kml、shp转dxf、shp修复。
rstool正在开发中,不定期更新,开源地址是https://github.com/ytkz11/rs-tool
欢迎来白嫖。
由于这个项目是个人项目,我的业余时间不大可能全部都投入到rstool的开发中,在我的预想中rstool集成的功能最好具备以下几个特点
1、具有通用性,尽可能地帮助到更多的同行
2、具有实用性,确确实实解决实际问题
3、具有稀少性,比如说现在这四个功能是比较少见的,其他软件没有具体的实现,若是其他的软件可以实现,那就使用其他的软件就好了,不要重复造轮子。
如果你有其他想实现的功能,集成到rstool中,可以在下方留言区留下你宝贵的建议。